Abstract
This study collected basic information for improving the Hanwoo cattle in the Gyeonggi region. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) markers in autosomes was estimated by analyzing the Hanwoo raised in the Gyeonggi region using the Hanwoo SNP 50K BeadChip. The Hanwoo tail hair samples used in this study were collected from 827 Hanwoo cattle in the Gyeonggi region and were subjected to SNP Chip analysis. Furthermore, 52,195 SNPs were obtained from the analysis. Quality control was performed to remove unnecessary SNPs, and 41,605 SNPs were obtained. The total genome length was 2,500.01 Mb, with chromosome 25 (42.65 Mb) being the shortest and chromosome 1 (158.09 Mb) being the longest. The r2 value was 0.231 for the SNP distance between 0 and 50 Kb and was 0.065 for distance between 150 and 200 Kb. Thus, the closer the distance between the SNPs, the higher the r2 value. Genetic improvement has been conducted for approximately 100 years in Angus and Holstein breeds. However, for the Hanwoo, genetic improvement has been conducted for approximately 40 years (Jo et al., 2012). In addition, the selection intensity for Hanwoo genetic improvement is lower than that of other varieties. This study confirmed that Hanwoo in the Gyeonggi region had no significant difference in LD. However, it is necessary to test cow to prevent the occurrence of inbreeding and reduction in genetic diversity caused by a preference for specific KPN.
Figures & Tables
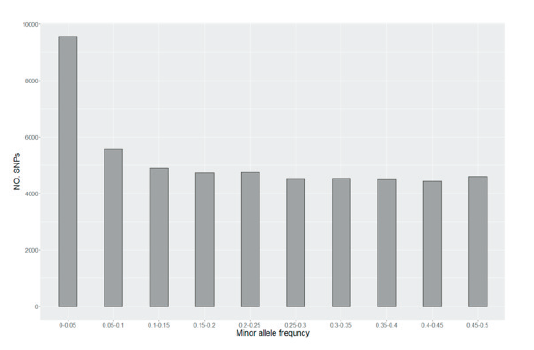
Fig. 1. Minor allele frequency (MAF) of SNPs


