Abstract
This study analyzed linkage disequilibrium (LD) and effective population size (Ne) to understand structural characteristics such as genetic diversity and historical events of the Hanwoo cow population using Illumina SNP50K BeadChip. The genomic DNA was prepared through the hair roots of 2,076 Hanwoo cows in Gyeongbuk province and 941 Hanwoo cows in Jeonbuk province, and a total of 53,866 and 50,908 SNP were obtained, respectively. For analysis, 2,058 samples and 41,449 SNP were selected in Gyeongbuk, and 941 samples and 35,863 SNP were selected in Jeonbuk through a QC. LD (r2) by the distance between pairwise SNP was calculated, and the average r2 was 0.05 ± 0.10 in Gyeongbuk, and 0.04 ± 0.07 in Jeonbuk. r2 was shown to be 0.23 ± 0.29 at 0-50 kb and 0.12 ± 0.19 at 50-100 kb in Gyeongbuk, and 0.21 ± 0.26 at 0-50 kb and 0.11 ± 0.18 at 50-100 kb in Jeonbuk. The past effective population size was 994 heads in 69 generation ago but decreased to 267 heads in 13 generation ago in Gyeongbuk, 1,588 heads in 70 generation ago but decreased to 415 heads in 13 generation ago in Jeonbuk. As a result, it was confirmed that LD decayed by the physical distance between SNP, and the genetic diversity of Hanwoo cows gradually declined. It might be in urgent need of a conservation plan that includes a cow-customized genetic management program.
Figures & Tables
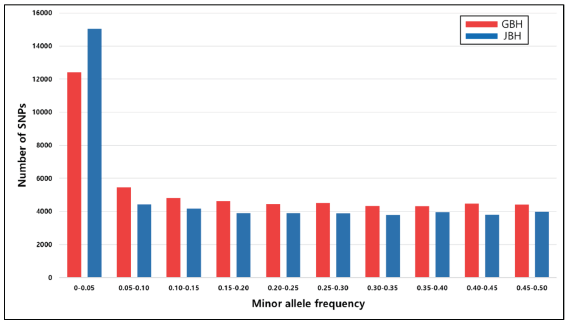
Fig. 1. Distribution and quantile-quantile plot (Q-Q plot) for carcass traits in 9,849 steers.


