Abstract
This study was conducted to use the Bayes approach, which can be applied in various pre-distribution for genomic selection application in the evaluation of Hanwoo carcass traits, as basic data for genomic selection through genetic accuracy and reliability estimation. As for the data used in the analysis, 8,413 DNA collected by various methods from Hanwoo farms nationwide were extracted. The Axiom Bovine 60k version 3(Affymetrix Inc., 2006) SNP panel was used to generate genomic information. Quality control removed SNPs whose SNPs were on sex chromosomes or whose position on chromosomes was not identified, with a total value of more than 64 markers removed, with an SNP call rate of 95% or less, a Minor Allele Frequency(MAF) of 0.01 or less, and a Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium(HWE). Among the 8,413 with genetic information, duplicate animals, pedigree errors, and animals that did not match dependent variables were removed, and 6,616 reference groups with genotype information were used for analysis. The KPN used in the analysis was extracted using semen, and the DNA was extracted using tissue samples provided by the Korea Institute for Animal Products Quality Evaluation, and in the case of cows, tail hairs were collected, and DNA was extracted and used for analysis. MBV accuracy was estimated to be 0.25 to 0.55, and accuracy is affected by various factors. In the case of clustering, it is considered that a change in MBV accuracy occurs because the composition of the training group and the verification group varies depending on the number of groups and the clustering method. In addition, MBV accuracy changed according to Bayes B and Bayes C methods assuming different prior distributions. Among the Bayesian methods, the accuracy of MBV in Bayes C was higher than that of Bayes B. This is believed to be because the assumption of prior distribution to estimate the SNP effect is different, and considering that there is no SNP with a great effect, Hanwoo slaughter data is quantitative, so it is considered that the genes involved are related to multiple genes, not a specific one. As genotype information was added to the existing phenotype information, the reliability of the Hanwoo carcass traits GEBV increased by 0.243±0.060. In particular, in the group with low reliability, the contribution to estimating the GEBV was low, but the increase in reliability was the highest. It was found that the ranking of genetic evaluation on phenotype data changed due to mixing with MBV. Compared to the GEBV, the Two Step method was more correlated than the Single Step method. Therefore, when using genotype information, the difference between the Single Step and the Two Step is not much different, but when a lot of genotype data is collected in the future, it is considered that there will be a difference in reliability and GEBV.
Figures & Tables
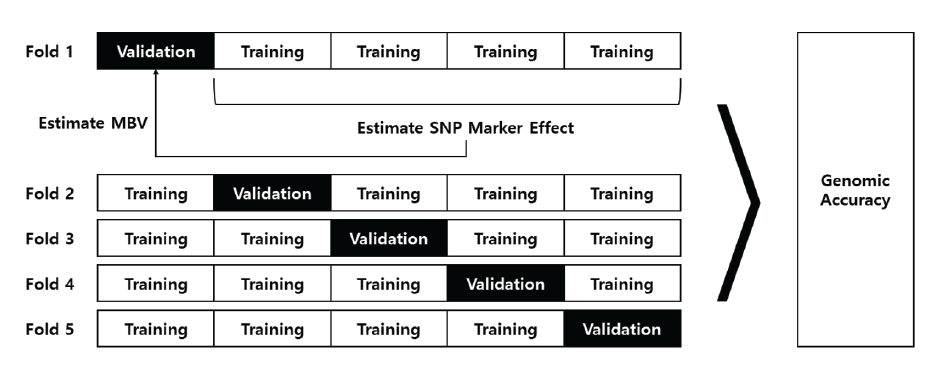
Fig. 1. Diagram for cross validation


