Abstract
Reproductive trait of cows are important factors affecting pregnancy and calving cycle, and a short calving cycle leads to increase productivity of livestock, so improvement is essential. However, the improvement standards for reproductive traits and studies on causative genes are insufficient. Therefore, in this study, GWAS (Genome-Wide Association Study) analysis was conducted on Hanwoo cow in the Gyeongsan provice. Heifer traits were FS (Age at 1st service), FCO (Age at 1st conception), FCA (Age at 1st calving) and 874 animals were used for analysis, and cow traits were GL (Gestation length), DO (Day open), CI (Calving interval), NS (Number of service) and 741 animals were used for analysis. Hanwoo 50K SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) BeadChiop was used for the genotype, and 37,903 SNP markers were used for the heifer trait and 38,011 SNP markers were used for the cow trait through the quality control option of less than 1% minor allele frequency, more than10% missing genotype, less than 10-6 HWE (Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium) on the PLINK 1.9. Thereafter, the genome-wide threshold level was determined using the Bonferroni method, and SNP marker were identified according to each trait. As a result, three SNP markers on chromosomes 12, 13, 24 in FS (ARS-BFGL-BAC-830, BTB-00532606, ARS-BFGL-NGS-33785), and two SNP markers on chromosomes 3, 20 in GL (BTA-94162-no-rs, Hapmap47647-BTA-50780), and two SNP marker on chromosomes 27, 28 in NS (ARS-BFGL-NGS-58109, BTB-00973399) were identified. Then, the seven candidate genes with the closest significant SNP markers were identified. Among them, PCK1 in FS is a gene that affects the promotion of progesterone activity, and it has been reported that it is helpful for reproductive efficiency by affecting follicle development and pregnancy rate. In the future, if additional research is conducted by setting up suitable models for reproductive traits and continuously increasing the test population, it is judged that it will be possible to clearly identify causative genes for each trait.
Figures & Tables
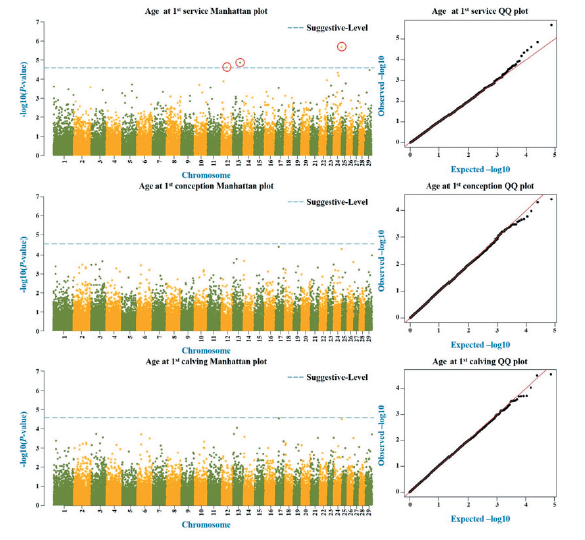
Fig. 1. GWAS results for FS, FCO and FCA are presented as Manhattan plot and Q-Q plot. (GWAS: Genome-wide association study; FS: Age at 1 service; FCO: Age at 1 conception; FCA: Age at 1 calving)


