Abstract
The purpose of this study was to analyze the novel single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the gap junction protein alpha 4 gene (GJA4) identified in horse muscle RNA-seq and to predict structural changes of proteins by SNPs. In our previous study, we observed differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Thoroughbreds before and after exercise through RNA-seq analysis. In addition, we conducted an evolutionary analysis using Thoroughbred and Jeju horse re-sequencing data. As a result, we discovered a novel SNP present in GJA4 (LOC22385534 C>G) in the evolutionarily selected gene in the Thoroughbred horse. Transcription factor (TF) binding sites in the 5′-regulatory region of this gene were identified via PROMO. Additionally, bioinformatics tools were used to predict the effect of non-synonymous SNPs (nsSNP) on function and stability. We identified the change of protein structure owing to the amino acid sequence change, which was proline to arginine according to nsSNP data. Our analysis will be useful as a basis for studying genes and SNPs that affect horses.
Figures & Tables
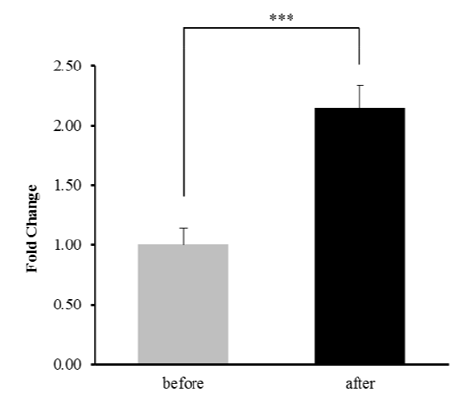
Fig. 1. The gene expression of GJA4 by RNA-seq before and after exercise. *** <0.001.


