Abstract
Quails which are commonly found in the small holder farmers in Indonesia is black and brown lines of Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). The objective of this study was to construct phylogenetic tree of black and brown Japanese quail based on Mitochondrial (mt) D-loop sequence. A total of nine quail blood samples has been collected to be furthermore used for DNA extraction. Polymerase chain reaction has been carried out to isolate 661 bp of D-loop region. Moreover, PCR product was analyzed to generate D-loop sequences. Nine D-loop sequences from samples and nine additional published sequences have been used to construct phylogenetic tree by MEGA 7.0. The result of phylogenetic reconstruction of 18 samples indicated that black and brown Japanese quail was located in the same clade that means no genetic variation found in the population. According to all sequences, a total of five haplotypes were observed with haplotype and nucleotide diversities of 0.68 and 0.059, respectively. In addition, the genetic distance among quails was ranged from 0.000 to 0.674 with average value of genetic distance was 0.300. In conclusion, black and brown Japanese quails in Indonesia were closely related each other and also relatively closed to published sequence of Japanese quail, and they were completely separated with other species of quails such as Coturnix chinensis based on D-loop sequence.
Figures & Tables
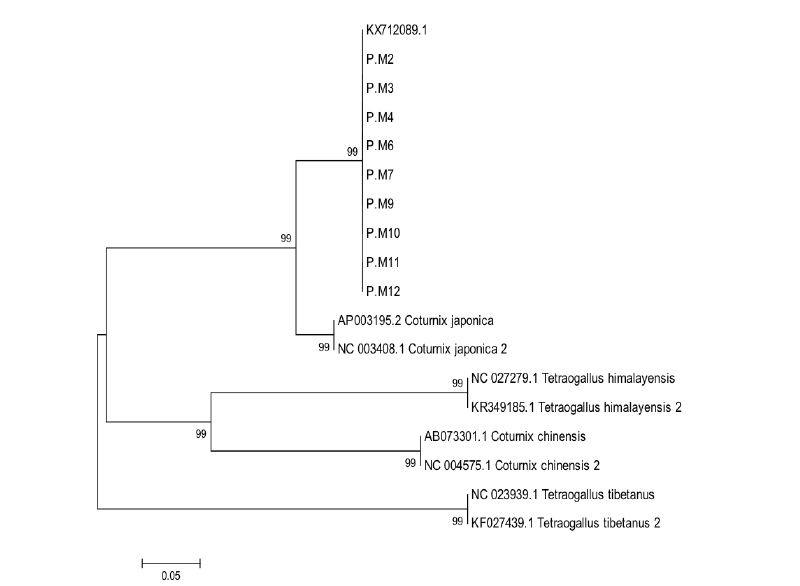
Fig 1. Phylogenetic tree of nine samples of Black and Brown Japanese quail and reference sequences obtained from NCBI database


