Abstract
This study was conducted to investigate the genetic parameters and trends using the carcass data of Hanwoo (Korean beef cattle). The traits to be analyzed were six of the back fat thickness, the longissimus muscle, the carcass weight, the intramuscular fat, the meat quality and quantity grade. The heritabilities estimated were 0.31, 0.34, 0.42, 0.43, 0.24, and 0.17, respectively, using the REML Animal model. In the genetic correlation, the back fat thickness showed positive correlations with the carcass weight, intramuscular fat and meat quantity grade of 0.31, 0.10, and 0.93, respectively, and negatively correlated with the longissimus muscle and meat quality grade of -0.06 and -0.13. The longissimus muscle was positively correlated with the carcass weight and intramuscular fat of 0.66 and 0.26, respectively, and negatively correlated with the meat quality and quantity grade of -0.25 and -0.36, respectively. Correlation between carcass weight and quality grade was 0.15 and 0.13, respectively. Correlation between carcass weight and meat quality grade was negative at -0.13. Intramuscular fat was negatively correlated with meat quality grade at –0.98. The annual genetic improvement estimated by simple regression was estimated to be -0.027mm in back fat thickness, 0.072cm2 in longissimus muscle area, 0.396kg in carcass weight, 0.011 in intramuscular fat score, -0.003, in meat quality point and -0.004 in meat quantity grade point, respectively.
Figures & Tables
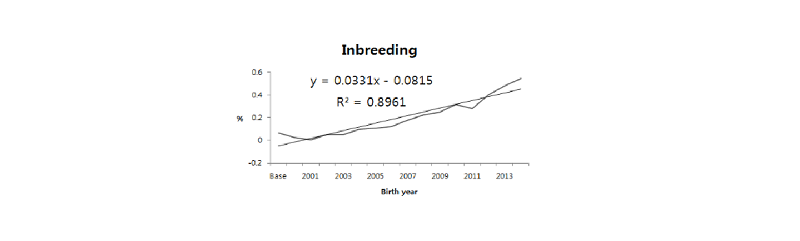
Trend of inbreeding coefficients in the Hanwoo population.


