Introduction
Acquiring an accurate pedigree in animal breeding studies have always been major concerns for animal breeders. Even to date, most of the pedigree records are collected by farmers or agency personnel which makes it difficult to avoid pedigree related errors completely. For this reason, animal breeding researchers have written various computer software packages to perform pedigree correction using basic principles of pedigree formation. Most of those softwares i.e., ASReml (Gilmour et al., 2009), WOMBAT (Mayer, 2007), BLUPF90 (Misztal et al., 2002), PEDIG (Biochard, 2002), CFC (Sargolzaei et al., 2006), and many R packages were mostly designed to perform statistical analysis on pre-processed pedigree. Although some packages offer arrays of functions or features for pedigree processing, those lack user-friendly environment and require some level of computing skills. This is because such packages were written mostly for a cleaned pedigree and used sophisticated programming languages i.e., FORTRAN, C or R to obtain higher computation efficiency. Some of them are machine platform (Windows or Linux) dependent too. As a common scenario, some packages might ignore errors through deletion of erroneous records and continue to next steps or even if reports error would be difficult to trace back.
Therefore, we report a pedigree management software package (Animal Genetic Evaluation Laboratory Pedigree Toolkit or AngelPedTk) which is designed to optimize user experiences greatly while ensuring computing efficiency as possible. This toolkit consists of a set of four modules featuring both basic command line interface (CLI) and a graphical user interface (GUI) environment. Basic precompiled modules are invokable through Windows command prompts independently, and run in batch-mode with other programs. However, the GUI interface is a wrapper module over these CLI based core precompiled executables offering many window-based front-end features for a smoother user control over the pedigree management and estimation processes. In other words, the GUI accepts required arguments and processed them through precompiled executables.
Computing Methods
AngelPedTk is a collection of four modules (CLI based executable) written in C programming language. Additionally, this software provides a GUI wrapper for these modules (Figure 1), written under Qt 4.8 software development framework, which creates an easy-to-use and user-friendly pedigree processing environment for users of no prior programming experiences. The core version of this toolkit (command line) are designed with overloading and optional parameters. Although runtime optimization was not our primary objective for simplicity sake, these programs execution are generally faster even with large datasets due to the advantages of low-level C language. We implemented a fairly a large hash-table data structure (max. 1,000,000 buckets) so that moderately larger pedigree datasets could be processed easily. This toolkit also supports larger animal ID (upto 32 alphanumeric characters) for which some widely used pedigree based softwares are limited.
Modules And Purposes
Four standalone modules included with this toolkit are designed for specific tasks. The primary functions of each module are summarized as bellow:
1.PedCheck – a tool for pedigree errors check,
2.PedTrace – a tool of creating sub-pedigree from a whole pedigree for given animals,
3.PedStack – a tool for complete pedigree stacking of given animals,
4.PedGetF – a tool for pedigree sorting (chronological ordering), renumbering, calculation of inbreeding, coefficients, and pedigree completeness index.
Although, we suggest a sequential execution in above listed order to obtain more control on pedigree processing, users can follow any order of executions if required input files are already prepared.
The PedCheck Module
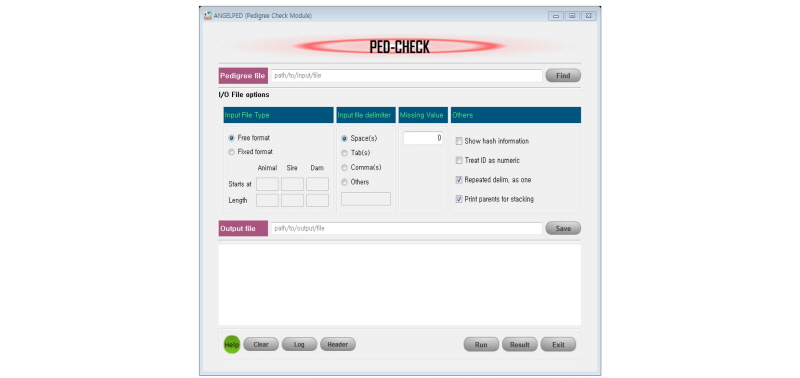
Typically, a pedigree file consists of three columns representing animal (progeny ID), sire, and dam, respectively. In practice, several types of pedigree errors could occur, mostly due to human errors. Generally, pedigree records are considered incorrect when an animal ID appears as (I) its own sire and/or dam, (II) a parent differently (sire and dam) between progenies, and iii) like error II except that its own pedigree is also missing. Additionally, duplicated animal records (rows) are often discouraged, even though those might not be errors in true sense. But these duplicated records could be expensive regarding memory and processing time, and thus are avoided as possible. PedCheck module searches for such errors and reports accordingly for necessary actions. As of features implemented, it supports both free or fixed format files with single or mixed data field delimiters (Table 1 & 2; Figure 2). By default, missing values are set to zero and all columns values are considered as alphanumeric type unless specified explicitly.
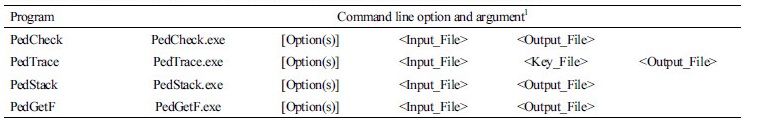
Table 1. Commands and arguments for tools in ANGELPED Toolkit on a windows platform
|
|
1 The orders of input, key and output files are important, whereas option sequences are insignificant |
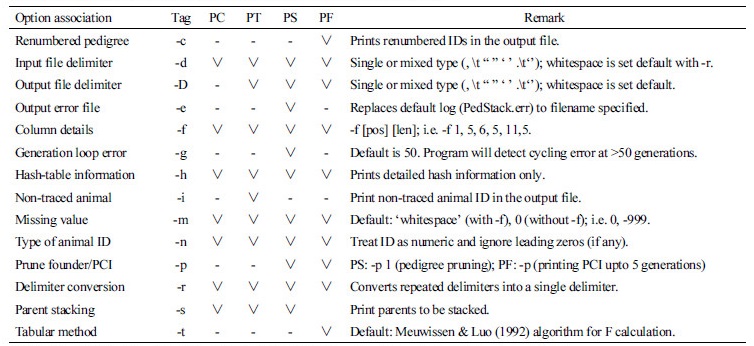
Table 2. List of command line arguments for tools in ANGELPED Toolkit1
|
|
1PC, PedCheck; PT,PedTrace; PS, PedStack; PF, PedGetF; PCI, Pedigree Completeness Index; F, Inbreeding coeffic |
The PedTrace Module
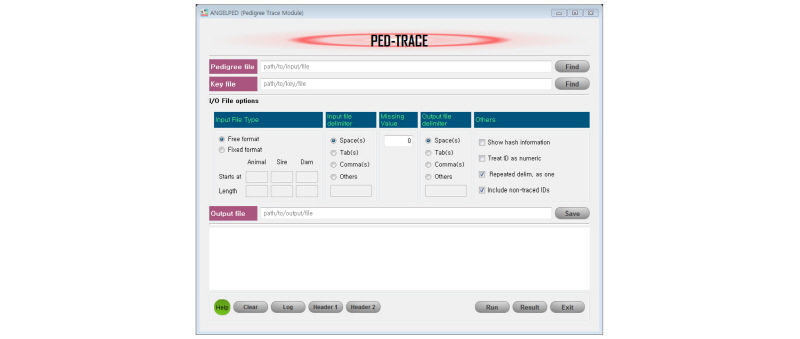
In animal genetic study, it is often found that pedigree files are obtained from a source as is, whereas a user may need a desired (reduced) pedigree for animals with phenotypic records only. This module is especially written for searching related pedigrees for such purposes. This program (Table 1 & 2; Figure 3) also shares many similar features as been implemented in PedCheck program. Note that a key file with animals listed is a requirement for this module. Non-traced animals can also be included in the output file. This pedigree processing phase is especially important in a sense that those unrelated pedigrees is unable to add extra relationship information to the model with respect to animal phenotypes. Instead, those unrelated pedigrees can increase data processing time significantly.
The PedStack Module
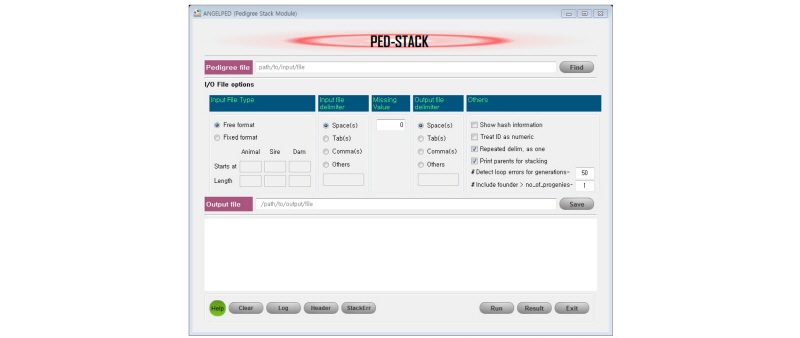
This module is written for generating a stacked pedigree structure according to generations. Usually, breeding values are estimated using Henderson’s mixed model equation (BLUP; Henderson, 1973), where animal relationships are accounted for capturing additive genetic variations. Calculating numerator relationship matrix (NRM) could be a tedious work if done by hand or even by computers, and therefore, different algorithms emerged over the years to improve computing efficiency. One of the most efficient algorithm is to stack animals according to generations where parents appear before progenies. This calculates relationships sequentially and avoids double counting of animals. Therefore, it reduces NRM creation time very significantly, even with larger pedigrees. However, animal ordering according to generations becomes difficult if birthday records are not kept at all or partial. So, with no dependency on birthdays, PedStack module uses an algorithm for ordering pedigrees by generations (Kim et al., 2006). By default, it is set to order animals upto 50 generations under the assumption that circular pedigree errors (progeny becomes ancestor of an ancestor) may occur where animal generation extends beyond 50. The PedStack module (Table 1 & 2; Figure 4) also allows pruning of parents in the founder group based on minimum number of progenies. The default value of 1 for pruning indicates that this parent has appeared only once in the progeny generation while its own pedigree is missing. Therefore, this parent will be discarded from or treated as missing in the output pedigree. These default features are easily modifiable too. Note that with prior knowledge of no existing errors in the raw pedigree and with no need for PedTrace phase, a user can directly proceed through PedStack step to generate a comprehensive stacked pedigree from the raw data.
The PedGetF Module
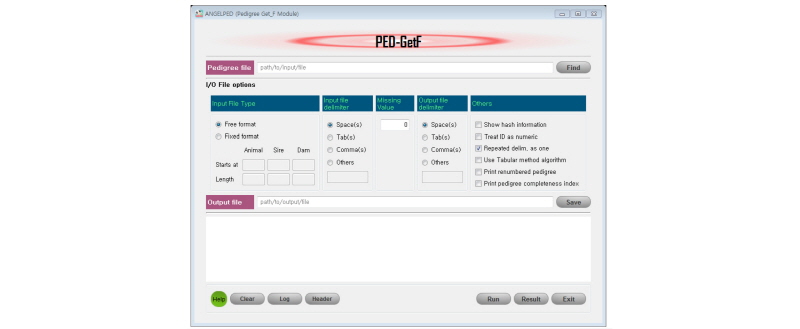
Animal breeding value estimation is commonly based on mixed-model equation (MME) using Henderson’s BLUP method. An essential step to do this is to obtain an inverse of relationship matrix A (additive genetic relationship) for animals. A is a symmetric matrix and its diagonal element for an animal i is equal to 1 + Fi, where Fi is the inbreeding coefficient of animal i (Wright, 1922). Over time clever and elegant but simple rules were coined to build the inverse of A (Henderson, 1976). Advanced concepts such as iteration on data concept (IOD; Schaeffer and Kennedy, 1986) can avoid the need for direct calculation of inbreeding coefficient as well. However, a simple decomposition of relationship matrix is known as A=TDT´ (Thompson, 1977), where T is a lower triangular matrix and D is a diagonal matrix for Mendelian sampling. A detail of this decomposition is found in Mrode (2014). In summary, to obtain an inverse of A, the diagonal element (Bii) of D-1 is needed (see NIAS, 2012 for calculating Bii). This module can compute Bii elements. For inbreeding coefficient calculation, we implemented Meuwissen and Luo (1992) algorithm as a default option. However, our observation showed that when the animals in pedigree are highly inbred, the computation of F using tabular method (see details in Tier, 1990) as attributed to Lush by Emik and Terrill (1949, cited by Hudson et al, 1982) deemed more efficient. PedGetF (Table 1 & 2; Figure 5) uses a variance covariance matrix (Henderson C.R., 1976) with an optional argument. The pedigree completeness index (PCI, MacCluer et al., 1983) usually provides information on the quality of a pedigree. We implemented a PCI computation algorithm as used in the PEDIG package by Boichard (2002). Instead of 8th generation tracking through PEDIG package, PedGetF module can produce upto PCI upto 5th generation. Note that an additional argument is required for obtaining PCI estimates in the output file.
Availability, platform compatibility and installation
AngelPedTK 1.0 software toolkit can be freely downloaded from http://www.nias.go.kr/. Both command line modules and modules with GUI wrappers are Windows platform specific and are distributed in both 32- and 64 bits formats. These are compiled binaries, complied by GNU gcc and Qt/C++ compilers. The GUI distribution provides all required Windows DLL files, so that it can be run without prior installation on user computers. We, however, do not provide Linux binaries but source codes are available by request for platform specific compilation.
Special GUI Features
The GUI of AngelPedTK 1.0 software implemented some convenient Windows OS specific features such as file browsing, “drag and drop” for file inputs, native windows look with Qt framework. The GUI includes a dedicated dashboard to provide a preview on the input and log files. This kit can utilize the system default text file editors (i.e. notepad) for previewing large output files and system default internet browsers to invoke help pages. Another helpful feature of the GUI module is the auto generation of output file names with respect to input files which, of course, can be modified easily according to user demands.