Background
miRNAs are a class of endogenous small non-coding RNAs, approximately 22 nucleotides in length, which play a role in post-transcriptional regulation by targeting mRNA degradation or inhibiting their translation (Jin et al., 2013).
Recently, we reported that three functional SNPs in the 3´untranslated region (3´UTR) of glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1, mitochondrial (GPAM) (GenBank NC_037353.1), which catalyzes the initial and committed step in glycerolipid biosynthesis, were significantly associated with marbling score. In addition, four putative miRNAs (bta-miR-2418, bta-miR-375, bta-miR-2479, and bta-miR-2468) were identified. The SNPs were located in the seed region of these miRNA (Kim et al., 2021, Yu et al., 2017). We found that g. 55930 C>T SNP was perfectly complementary to the bta-miR-2468 seed region, congruent with the results reported by Kim et al. (2021). We choose bta-miR-2468 and g. 55930 C>T SNP with calculating the minimum free energy (MFE) for each allele in the g. 55930 T>C SNP for the best in the experiment; T>C substitution decreased the predicted MFE from 0 to –19.8 kcal/mol. These in silico results indicated that g. 55930 C>T could affect the bta-miR-2468 related regulation of GPAM by changing its binding affinity.
In this study, we aimed to investigate whether bta-miR-2468 binds to the 3´UTR of GPAM, including the g. 55930 C>T SNP, and whether each allele of this SNP affects the binding affinity between the target miRNA and the 3´UTR.
pmirGLO recombinant vector, transfection, and dual luciferase assay
For the dual-luciferase assay, which allow study of protein expression or regulation in cells with the firefly luciferase and renilla luciferase activities of the sample, two oligo variants (g. 55930 C and g. 55930 T) containing the polymorphic site and bta-miR-2468 binding site, were synthesized directly and cloned into pmirGLO dual-luciferase reporter plasmids using the restriction enzymes Sac I and Xho I. The resulting constructs were designated pmirGLO-55930 C and pmirGLO-55930 T, respectively. The sequences of the constructs were verified using Sanger DNA sequencing. HEK293T cells were sub-cultured in a 96-well culture plate for 24 hours before transfection in growth media supplemented with 10 % FBS and 100 IU/mL penicillin/mg/mL streptomycin, at 37 ℃ in a 5 % CO2 atmosphere. After reached 70 - 80% cell confluency, the bta-miR-2468 mimic or Negative control miRNA mimic was co-transfected with the reporter vector (pmirGLO-55930 C and pmirGLO-55930 T) using Lipofectamine 3000 in triplicate. Luciferase activity was measured 48 hours after transfection using the Dual-Luciferase® Reporter Assay System (Promega). Results were normalized to the activity of firefly luciferase and renilla luciferase (Li et al., 2019, Alvarez 2014, Heyn et al., 2013., Tomasello et al. 2019). Student’s t-test was used to compare two different groups; p>0.05 was considered statistically significant.
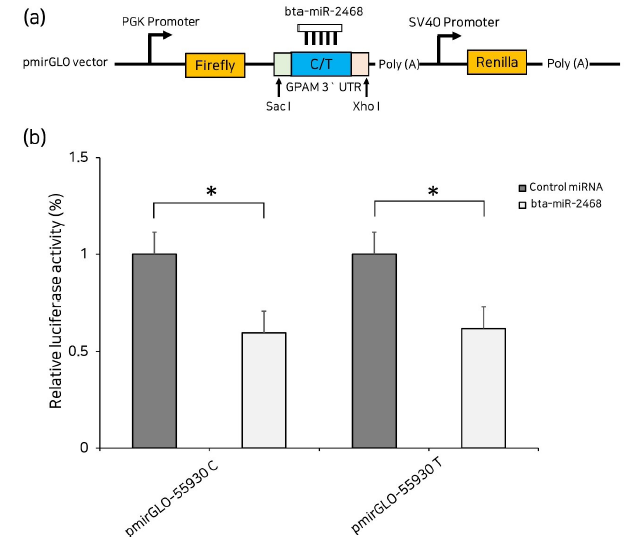
Fig. 1. bta-miR-2468 binding to GPAM 3´UTR. (a) Schematic representation of the dual luciferase assay for C and T alleles. (b) Relative luciferase activities are similar to C and T alleles with bta-miR-2468, as compared with negative control miRNA in HEK293T cells. Error bars (SE) are derived from three independent experiments performed in triplicate, and data were compared using a Student’s t-test. * p<0.05
bta-miR-2468 binding to GPAM and effects of the g. 55930 T>C SNP on binding affinity
We performed a dual-luciferase assay to validate the in silico results reported by Kim et al. (2021).
Kim et al. (2021) reported that when either g. 55930 C or g. 55930 T were present in the seed region of bta-miR-2468, there was an evident reduction in the relative luciferase activity in HEK293T cells (p<0.05). However, co-transfection of both the g. 55930 C allele, T allele and bta-miR-2468 did not result in significantly different luciferase activities in HEK293T cells.
Here, we demonstrate the importance of post-transcriptional regulation of GPAM gene expression by bta-miR-2468. Considering the effect of haplotype (g. 54853 A>G - g. 55441 A>G - g. 55930 C>T) reported by Kim et al. (2021), the effect of the g. 55930 T>C SNP should be evaluated in future studies using pmirGLO vectors, including haplotypes.


